Azerbaijan AIRLINES EMBRAER 190's flight data recorder traces indicate the damage that the crew had to deal with after TWINJET was inconvenient due to explosions in Russian airspace.
The E190 has maintained multiple penetration shocks from a flagment that damaged the hydraulic circuit tube, a reservoir, a stabilizer pitch trim electric driving, and a fragment that had damaged ebening, including fins, elevators, and ladder.
Similar damage affected the left and left GE aerospace CF34 engines.
On December 25, the crew of aircraft operating the Baku-Grozny service loses the GPS navigation function, has encountered difficult weather conditions such as haz, decrease in visibility, and about 240 to 420m cloudy clouds. , I abandoned the attempt to land in the capital of Chechen. (790-1,380ft).
After the pilot chose to return to Baku, the aircraft climbed 3,500 feet.

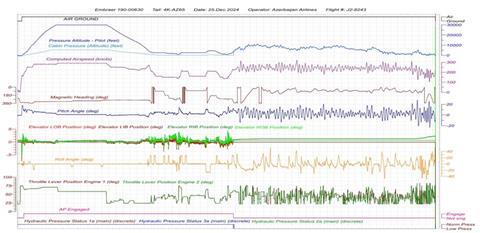
The Flight-Data Recorder Trace has revealed that the autopilot has been released and all hydraulic pressure has been blown off in the next 23s before hearing another bang.
The data provided in the preliminary survey of the committee indicates that the routine variations of both the invoords and boards stop, and the elevator traces are flat lines at a slightly different position.
The altitude of the cabin began to rise immediately, consistent with the actual altitude of the E190 after about 20s, indicating the suppression.
The aircraft, which had been cleaned up to 15,000 feet, continued to climb up to about 8,000 feet, then returned to about 6,000 feet and climbed 10,000 feet again.
According to the committee, a warning of the cabin height rang and repeated eight times. One of the pilots notifies the Grossney Tower that the aircraft could not go to 15,000 feet and said, “I can't maintain it (flight level) 150, the cabin has high pressure.”
The pilot also stated that the aircraft had “lost control,” and said he had suffered hydraulic failure.
About 14 minutes after the explosion, the Grosney Tower moved a flight to the Lostov Controller. The crew told Rostov that the aircraft was heading to Baku, and the controller instructed to maintain 9,000 feet.
The pilot told Rostov that the aircraft engine was running, but the Aileron and the elevator control system failed because of the recommendation of Mahakara for a detour, and declared that it was heading to Kazakhstan's Actau.
The data from the flight recorder constantly operates the thrust lever over half of the range to stabilize the flight path of the aircraft crossing the Caspian Sea, and delays them over half of the range and delayed them, and set them. It indicates that it is used.
As a result of the difficulty of control, the aircraft fluctuated in both the horizontal and vertical directions, continuously rolled from left to right, and sometimes exceeded 40 °.
The recorder trace suggests that the pitch is similarly unstable, and alternately performs about 10-20 ° nose -up and about 10 ° nose down alternately.

Aircraft captains had a considerable experience of flying the Embraer E-Jet family, with a total of 15,000 hours or more exceeding 7,000h. The first -class seabers had much less experience and only 830 hours in total, but they contained 670H in the electronic jet.
Among them, they nursing the aircraft to acta. The attempt to land on the runway 11 eventually failed. The aircraft dropped about 5 km crash northwest of the airport.
Both pilots were one of the 38 dead, but two residents (29, including two hut crew members, survived.
Azerbaijan President Ilham Ariev praised the efforts of pilots and flight attendants during the event in early January and said, “If the pilot did not demonstrate such exceptional professionalism and courage. There would have been no survivors from the incident. “


